Skin cancer is similar to most types of cancer where a known, single cause has not been found. Most cancers seem to be the result of a complex mix of many risk factors such as life style choices, exposure to known cancer-causing substances in the environment. The frequency and accumulation of the exposure to a risk factor increases the chances that cancer will develop. Therefore it may take many years for cancer to develop after exposure to a risk factor.
People may be exposed to several risk factors in the course of their daily lives. Some of these risk factors such as the sun and tobacco can be avoided, while others like age or genetic factors cannot. At least 50% of cancers can be prevented through healthy living. Risk reduction (or prevention) means taking action to lower the risk of developing cancer. There are ways a person can decrease his/her overall chance of developing certain types of cancer and stay well. In the case of skin cancer one of the vital ways to reduce risk is to avoid over exposure to the sun.
DO NOT GET A SUN BURN
Cover Up
Wear long clothing, broad brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses.
Dark coloured and tightly woven fabrics (Polyester/Lycra) are the most protective. If you can see through the material then the UV rays can get through especially when the fabric is wet. Most light cotton T-shirts have less protection than sunscreen with SPF rating of 15. Keep newborns out of the sun. Children under age of 6 months should keep out of direct sunlight. Sunscreens should be applied to all exposed skin.
Wear Sunglasses
The sunglasses should be labeled to block 99-100% of UVA abd UVB rays or UV absorption up to 400 nm, or meets ANSI UV requirements.
Wear Sunscreen
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF of 15 or higher every day, even the winter. Apply approximately 30 minutes before going out into the sun to allow for absorption. The sunscreen should be reapplied every 2 hours or after swimming or excessive sweating. Even sunscreens that are labeled waterproof should be reapplied after swimming. The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) system is not a linear system as commonly believed. The SPF numbers refers to the number of minuets a person can spend in the sun before getting equivalent of one minuet of UVB rays.
SPF 15 sunscreens filter out about 93% of UVB rays and after an hour in the sun the person has equivalent of four minutes of protection free sun exposure.
SPF 30 sunscreens filter out about 97% and after an hour the equivalent exposure is only two minutes.
SPF 50 sunscreens filter out about 98% and SPF 100 filters out about 99%.
Be especially vigilant in wearing sunscreen near water, snow and sand. These surfaces reflect the UV rays and can increase the risk of sun damage. Snow can reflect 80% of the UV rays.
Seek the Shade especially between 10 am and 4 PM
Use the shadow rule: If your shadow is shorter than you- Seek Shade. When shadows are shorter than objects creating them, avoid direct sunlight. When the shadow and object are equal in length you should restrict sun exposure to approximately ½ hour. When the shadows are twice the length of the objects you can spend an hour in the sun.
Avoid UV Tanning Booths
Despite the claims of the tanning booth industry, tanning booths are not safe. The lamps used in tanning beds give out UVA rays and often UVB rays as well. These ultraviolet rays have been shown to cause serious long-term skin damage and are may be a risk factor for skin cancer.
Even people who make healthy choices and do everything they can to reduce their risk, can develop cancer. Some people develop cancer without having any identifiable risk factors.
Causes of Melanoma
There is no single cause of melanoma, but there are some factors that increase the risk of developing it. These are factors you should note such as exposure to UV radiation. Ultraviolet B radiation has been shown to be a tumor initiator and a tumor promoter. Sunlight exposure acts in a cumulative nature where the cancers often appear after decades of damaging exposure.
How to Identify Malignant Melanoma
The best way to identify melanoma is to notice changes in normal skin or mole. These changes can occur over several months to years.
Using the ABCDE Rule
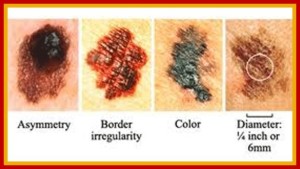
Asymmetry: shape of one half does not match the shape of the other half/
Border: irregular borders or jagged edges may become blotchy or blurry the pigment may spread and seep into the surrounding normal skin.
Colour: more than one colour – may be shades of black, brown, or blue and sometimes white part of the mole may lose colour.
Diameter: any increase in size, more than 6mm in diameter – bigger that the end of an eraser this growth may be slow or very rapid.
Evolution: any change in size, shape, elevation, surface, or colour of the mole.
Herbs good for skin
These herbs are actually known for the cancer prevention and in some contexts treatment. Always best to see your naturopath for specifics.
- Astragalus
- Bitter Melon
- Cat’s Claw
- Ginger Panax Ginseng
- Grape seed extract
- Kelp
- Mistletoe
- Nerium Oleander
- Turmeric
Nutritional supplements
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C and bioflavanoids
- Coenzyme Q10
- Melatonin
- Zinc
Foods rich in bioflavonoids and vitamin C like all the blues, red and yellows. For those who have no sensitivity to soy, one of its constituents; genistein, has been found to help with skin and breast cancers – Juicing is also a great way to get beta carotene and other nutrients good for the skin.
Carrot juice with ginger, spinach, celery, beet and apple.
Or
Berry smoothie with blue berry, black berry, strawberry and raspberries.
Remember!
Prevention is Best, No long sun exposures, Wear sun screen, Have fun!!
Yours in Health,
Dr. Quinn Rivet, ND



